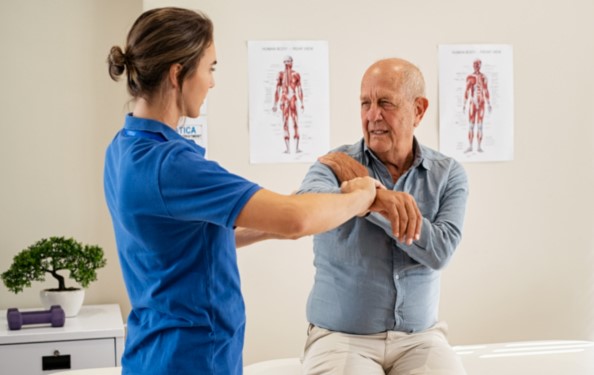
Can Exercise Therapy Help Manage Chronic Pain? Benefits & Tips
Chronic pain is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, making it difficult to perform daily tasks and participate in activities they enjoy. For many people with chronic pain, finding an effective solution can be a long and frustrating journey.
One potential solution that has gained increasing attention in recent years is exercise therapy. Exercise therapy involves a range of physical activities designed to improve strength, flexibility, and overall physical function. It has been shown to be effective in managing a wide variety of health conditions, including chronic pain.
In this article, we will explore the question of whether exercise therapy can help manage chronic pain. We will examine the benefits of exercise therapy, cite relevant studies, and offer tips for developing and maintaining an exercise routine. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how exercise therapy can be an effective tool in managing chronic pain.
What is Chronic Pain?
Before delving into how exercise therapy can help manage chronic pain, it’s important to define what we mean by chronic pain and understand its causes.
Chronic pain is pain that persists for an extended period, typically longer than three months. Unlike acute pain, which is a normal bodily response to injury or tissue damage, chronic pain is often not directly related to any injury or underlying medical condition.
There are many potential causes of chronic pain, including conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathy, as well as previous injuries or surgeries. In some cases, chronic pain may have no clear cause and be classified as “chronic non-specific pain.”
Regardless of the cause, chronic pain can have a significant impact on an individual’s physical and emotional well-being, leading to decreased activity levels, poor sleep, anxiety, and depression. It is important to manage chronic pain effectively to prevent these negative outcomes and improve overall quality of life.
How Exercise Therapy Can Help
Exercise therapy is a promising approach to managing chronic pain. Research has shown that regular physical activity can help alleviate pain symptoms and improve physical function. Here are some of the benefits of exercise therapy for managing chronic pain:
- Reduced pain intensity: Exercise has been shown to reduce pain intensity in people with chronic pain. Regular physical activity helps to release endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers, which can help to alleviate pain symptoms.
- Improved physical function: Chronic pain can make it difficult to perform daily tasks and participate in activities. Exercise therapy can improve strength, flexibility, and overall physical function, making it easier for individuals with chronic pain to perform activities of daily living.
- Reduced reliance on medication: Exercise therapy can help reduce reliance on medication for pain management. This is particularly important given the potential side effects of pain medications, including addiction, tolerance, and gastrointestinal problems.
- Improved mental health: Chronic pain can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health, leading to anxiety and depression. Exercise therapy has been shown to improve mood and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
When it comes to the types of exercises that can be beneficial for chronic pain sufferers, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, some types of exercise that have been shown to be particularly helpful include:
- Aerobic exercise: Aerobic exercise, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can help improve cardiovascular health, reduce pain symptoms, and increase overall physical function.
- Strength training: Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting or resistance band exercises, can help build muscle mass and improve overall physical function.
- Stretching: Stretching exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can help improve flexibility and reduce pain symptoms.
It is important to note that exercise therapy should be tailored to the individual and their specific needs and abilities. Working with a physical therapist or other qualified healthcare professional can help ensure that the exercise therapy program is safe and effective.
Studies on Exercise Therapy and Chronic Pain
Numerous studies have investigated the effectiveness of exercise therapy for managing chronic pain. Here are a few examples of studies that support the use of exercise therapy:
- A systematic review and meta-analysis published in the Journal of Pain in 2017 found that exercise therapy is effective in reducing pain intensity and improving physical function in people with chronic low back pain. The review analyzed 23 randomized controlled trials involving over 2,600 participants.
- A randomized controlled trial published in the Annals of Internal Medicine in 2016 found that a 12-week exercise program consisting of aerobic exercise and resistance training was effective in reducing pain intensity and improving physical function in older adults with knee osteoarthritis.
- A randomized controlled trial published in JAMA Internal Medicine in 2018 found that a 12-week exercise program consisting of aerobic exercise and resistance training was effective in reducing pain intensity and improving physical function in people with fibromyalgia.
Overall, these studies and others have consistently found that exercise therapy is an effective tool for managing chronic pain. Exercise therapy can help reduce pain intensity, improve physical function, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals with chronic pain.
Working with a Physical Therapist
Working with a physical therapist can be an effective way to develop an exercise therapy plan for managing chronic pain. A physical therapist is a healthcare professional who is trained to assess, diagnose, and treat movement-related conditions, including chronic pain.
Here’s how a physical therapist can help someone with chronic pain develop an exercise therapy plan:
- Assessment: The physical therapist will conduct an initial assessment to evaluate the individual’s pain symptoms, medical history, and physical function. This assessment will help the physical therapist develop an individualized exercise therapy plan that is tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
- Goal setting: The physical therapist will work with the individual to set realistic goals for their exercise therapy plan. Goals may include reducing pain symptoms, improving physical function, or increasing overall activity levels.
- Exercise selection: The physical therapist will select exercises that are appropriate for the individual’s specific needs and abilities. Exercises may include aerobic exercise, strength training, stretching, or a combination of these.
- Instruction: The physical therapist will provide instruction on how to perform the exercises safely and effectively. This may include demonstrating the exercises and providing feedback on form and technique.
- Progression: The physical therapist will monitor the individual’s progress and adjust the exercise therapy plan as needed. This may include increasing the intensity or duration of exercises as the individual’s physical function improves.
Working with a physical therapist can help ensure that the exercise therapy plan is safe, effective, and tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities. It is important to follow the physical therapist’s recommendations and guidance closely to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Tips for Developing an Exercise Routine
Developing a successful exercise routine can be a key component of managing chronic pain. Here are some tips for developing an exercise routine that can help manage chronic pain:
- Start slowly: It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise over time. This can help prevent injury and minimize pain symptoms. Begin with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity as your physical function improves.
- Pacing: Pacing involves balancing periods of activity with periods of rest. This can help prevent overexertion and minimize pain symptoms. Plan your exercise routine with regular rest breaks and avoid pushing yourself too hard.
- Variety: Incorporate a variety of exercises into your routine to avoid boredom and prevent overuse injuries. Try a mix of aerobic exercise, strength training, and stretching.
- Consistency: Consistency is key when it comes to exercise therapy. Make exercise a regular part of your routine, and try to stick to a schedule.
- Listen to your body: It’s important to listen to your body and adjust your exercise routine as needed. If you experience pain or discomfort during exercise, adjust the intensity or type of exercise accordingly.
- Seek professional guidance: Working with a physical therapist or other qualified healthcare professional can be helpful in developing a safe and effective exercise routine. They can provide guidance on exercise selection, technique, and progression.
By following these tips, you can develop a successful exercise routine that can help manage chronic pain and improve physical function. Remember to start slowly, pace yourself, and listen to your body to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Tips for Maintaining an Exercise Routine
Maintaining an exercise routine for the long-term can be challenging, but it is an important component of managing chronic pain. Here are some tips for staying motivated and accountable when it comes to exercise therapy:
- Set realistic goals: Setting realistic goals can help you stay motivated and focused. Break your goals down into smaller, achievable steps and track your progress along the way.
- Find a workout buddy: Having a workout buddy can provide accountability and motivation. Consider finding a friend or family member to exercise with or join a group exercise class.
- Mix it up: Adding variety to your exercise routine can help prevent boredom and keep things interesting. Try new exercises or activities to keep things fresh.
- Use technology: There are many apps and wearable devices that can help track your exercise progress and provide motivation. Consider using a fitness tracker or exercise app to help you stay on track.
- Reward yourself: Rewarding yourself for reaching your exercise goals can provide motivation and a sense of accomplishment. Treat yourself to something you enjoy, like a massage or a favorite meal.
- Be flexible: Life can be unpredictable, and it’s important to be flexible when it comes to your exercise routine. If you miss a workout or have to adjust your schedule, don’t get discouraged. Just get back on track as soon as you can.
- Remember the benefits: Remind yourself of the benefits of exercise therapy, such as improved physical function, reduced pain symptoms, and better overall health. Keeping these benefits in mind can help you stay motivated and committed to your exercise routine.
By staying accountable and motivated, you can maintain an exercise routine for the long-term and reap the benefits of exercise therapy for managing chronic pain.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle Factors
Diet and lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on chronic pain. Here’s how:
- Inflammation: Chronic pain is often associated with inflammation, and diet can play a role in reducing or exacerbating inflammation. A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to inflammation, while a diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for managing chronic pain. Excess weight can put additional stress on joints and exacerbate pain symptoms.
- Physical activity: Regular physical activity is an important component of managing chronic pain, but it can be difficult to achieve without a healthy diet. Eating a balanced diet that provides the energy and nutrients needed for physical activity can help make exercise therapy more effective.
- Sleep: Chronic pain can disrupt sleep, which can in turn exacerbate pain symptoms. Making positive changes to diet and lifestyle habits, such as avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed, can help improve sleep quality.
Here are some tips for making positive changes to diet and lifestyle habits to help manage chronic pain:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Avoid processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Work with a healthcare professional to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise therapy.
- Stay active: Incorporate regular physical activity into your routine, with guidance from a physical therapist or healthcare professional.
- Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate pain symptoms. Find stress-management techniques that work for you, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and make positive changes to your sleep environment and routine.
By making positive changes to diet and lifestyle habits, you can help manage chronic pain and improve overall health and well-being.
Other Pain Management Techniques
While exercise therapy can be an effective tool for managing chronic pain, it is often most effective when used in conjunction with other pain management techniques. Here are some other pain management techniques that can be used alongside exercise therapy:
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage chronic pain. There are many different types of pain medications available, including over-the-counter pain relievers, prescription medications, and opioid medications. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional when using pain medications to minimize the risk of addiction, tolerance, and other negative side effects.
- Mind-body techniques: Mind-body techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and tai chi, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can in turn reduce pain symptoms.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of talk therapy that can help individuals with chronic pain manage their thoughts and emotions related to pain. CBT can help individuals develop coping strategies and improve overall mental health.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. It has been shown to be effective in reducing pain symptoms in some individuals with chronic pain.
- Massage therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension and promote relaxation, which can in turn reduce pain symptoms.
It is important to take a multi-faceted approach to managing chronic pain, incorporating a range of pain management techniques as appropriate. Working with a healthcare professional can help ensure that the pain management plan is safe and effective, and tailored to the individual’s specific needs and abilities.
Conclusion
Exercise therapy is a promising tool for managing chronic pain. It has been shown to reduce pain intensity, improve physical function, and enhance overall quality of life for individuals with chronic pain. Whether you’re living with chronic pain or supporting someone who is, exercise therapy can be an effective and safe option for pain management.
If you’re considering exercise therapy for chronic pain management, remember that it is important to work with a qualified healthcare professional to develop an individualized exercise plan that is tailored to your specific needs and abilities. It’s also important to take a multi-faceted approach to pain management, incorporating a range of techniques as appropriate.
With dedication, patience, and guidance from a healthcare professional, exercise therapy can be a powerful tool for managing chronic pain and improving overall physical and mental well-being. Don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support on your pain management journey.
How Home Physiotherapy Can Help You Recover Faster After Injury | Benefits, Exercises & More
After an injury, it is common to experience pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Recovering from an injury can be a lengthy and frustrating process, but the good news is that there are ways to speed up the recovery process. One effective method is home physiotherapy.
Home physiotherapy is a form of physical therapy that can be performed in the comfort of your own home. It involves a variety of exercises, stretches, and movements that are designed to help you recover from an injury and improve your overall physical function.
The benefits of home physiotherapy are numerous. Not only is it a cost-effective alternative to in-clinic physiotherapy, but it also provides the convenience of being able to perform exercises in your own familiar surroundings. In this article, we will explore the importance of recovering faster after an injury and how home physiotherapy can help you achieve that goal.
Understanding Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, is a healthcare profession that specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of injuries, disabilities, and disorders affecting the musculoskeletal system. Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in injury recovery, as it helps to restore and improve the physical function and mobility of the affected area.
Home physiotherapy is a type of physiotherapy that is performed in the comfort of one’s own home. There are various types of physiotherapy techniques that can be used in home physiotherapy, depending on the type and severity of the injury.
Some common techniques used in home physiotherapy include:
- Range of motion exercises: These exercises involve moving the affected area in different directions to improve its flexibility and range of motion.
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises help to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, which can help to improve its stability and reduce the risk of reinjury.
- Stretching exercises: These exercises help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension, which can help to alleviate pain and stiffness.
- Manual therapy: This technique involves hands-on manipulation of the affected area to help reduce pain, improve mobility, and promote healing.
By using a combination of these techniques, a physiotherapist can create a customized treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs and goals. In the next section, we will explore the benefits of home physiotherapy in more detail.
Benefits of Home Physiotherapy
Home physiotherapy offers numerous benefits that make it a great option for those recovering from an injury. Here are some of the key advantages of home physiotherapy:
- Comfort of familiar surroundings: One of the biggest benefits of home physiotherapy is that it allows you to perform exercises in the comfort of your own home. This can be especially beneficial for those who feel anxious or uncomfortable in a clinical setting.
- Flexibility of scheduling: Home physiotherapy allows for greater flexibility in scheduling. You can work with your physiotherapist to create a schedule that fits your needs and lifestyle, whether that means scheduling sessions before or after work, on weekends, or during lunch breaks.
- Cost-effectiveness compared to in-clinic physiotherapy: Home physiotherapy is often a more cost-effective alternative to in-clinic physiotherapy, as it eliminates the need for travel and facility fees.
In addition to these benefits, home physiotherapy also allows for greater individual attention from a physiotherapist, as they can focus solely on your needs and progress. It also offers a level of privacy that may be preferred by some individuals.
By choosing home physiotherapy, you can take control of your recovery process and work towards achieving your goals in a comfortable and convenient setting.
Preparing for Home Physiotherapy
Before starting home physiotherapy, it is important to properly prepare yourself and your space to ensure that you can perform the exercises safely and effectively. Here are some steps you can take to prepare for home physiotherapy:

- Setting up a designated space for physiotherapy exercises: Designate a specific area in your home where you can perform the exercises comfortably and without interruption. This could be a spare room, a corner of a room, or even a cleared-out space in your garage or backyard.
- Obtaining necessary equipment and tools for the exercises: Depending on the type of exercises your physiotherapist has prescribed, you may need to obtain some equipment or tools to perform them safely and effectively. This could include items such as exercise bands, foam rollers, or weights.
- Finding a qualified physiotherapist to guide you through the process: It is important to work with a qualified and experienced physiotherapist who can guide you through the home physiotherapy process. Your physiotherapist will be able to create a customized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and goals, as well as monitor your progress and make adjustments as needed.
When looking for a physiotherapist, be sure to choose someone who is licensed and accredited in your area, and who has experience with the type of injury you are recovering from. You may also want to consider factors such as their availability, pricing, and location when choosing a physiotherapist.
By properly preparing yourself and your space for home physiotherapy, you can set yourself up for success and ensure that you are able to perform the exercises safely and effectively.
Common Injuries That Can Be Treated with Home Physiotherapy
Home physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option for a wide range of injuries, from minor sprains and strains to more serious injuries requiring surgery. Here are some common injuries that can be treated with home physiotherapy:
- Sprains and strains: Home physiotherapy can help to reduce pain and stiffness and improve mobility in the affected area. Examples of sprains and strains that can be treated at home include ankle sprains, hamstring strains, and wrist sprains.
- Back pain: Home physiotherapy exercises can help to strengthen the muscles in the back and improve flexibility, which can help to reduce pain and prevent future injuries.
- Post-surgical rehabilitation: Home physiotherapy can be an effective way to recover after surgery, as it allows you to perform exercises in a comfortable and familiar environment. Examples of post-surgical rehabilitation that can be done at home include knee replacement surgery and rotator cuff surgery.
Studies have shown that home physiotherapy can be just as effective as in-clinic physiotherapy for many types of injuries. For example, a study published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery found that home physiotherapy was just as effective as in-clinic physiotherapy for patients recovering from a total knee replacement.
Another study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found that patients who received home physiotherapy for a rotator cuff tear had similar outcomes to those who received in-clinic physiotherapy, with both groups experiencing significant improvements in shoulder function and pain reduction.
Overall, home physiotherapy can be an effective and convenient treatment option for a wide range of injuries, and studies have shown that it can produce significant improvements in pain, mobility, and function.
Home Physiotherapy Exercises
Home physiotherapy involves a variety of exercises and stretches that are designed to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility in the affected area. Here are some common types of exercises and stretches that can be performed at home:

- Range of motion exercises: These exercises involve moving the affected area in different directions to improve its flexibility and range of motion. Examples include shoulder circles, ankle rolls, and wrist bends.
- Strengthening exercises: These exercises help to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, which can help to improve its stability and reduce the risk of reinjury. Examples include squats, lunges, and resistance band exercises.
- Stretching exercises: These exercises help to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension, which can help to alleviate pain and stiffness. Examples include hamstring stretches, calf stretches, and neck stretches.
When performing home physiotherapy exercises, it is important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the exercises as your body becomes stronger and more flexible. It is also important to work with your physiotherapist to ensure that you are performing the exercises correctly and safely.
Here are some tips for developing and maintaining a consistent exercise routine:
- Set realistic goals: Start with small goals and work your way up. Celebrate each accomplishment along the way, and don’t get discouraged if progress is slow.
- Create a schedule: Set aside specific times each day for your home physiotherapy exercises. This will help you stay on track and make it easier to develop a consistent routine.
- Find an accountability partner: Enlist the help of a friend, family member, or physiotherapist to hold you accountable and provide support and encouragement.
- Mix it up: Try different types of exercises and stretches to keep things interesting and prevent boredom.
By following these tips and consistently performing your home physiotherapy exercises, you can help to speed up the recovery process and improve your overall physical function and mobility.
Monitoring Progress
Monitoring progress is an important part of the home physiotherapy process, as it allows you to track your recovery and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed. Here are some reasons why monitoring progress is important:
- Identifying areas of improvement: By monitoring progress, you can identify areas where you are making progress and areas where you may need to focus more attention.
- Motivation: Seeing progress can be a powerful motivator and can help you stay on track with your home physiotherapy exercises.
- Making adjustments: If you are not seeing the progress you had hoped for, monitoring can help you and your physiotherapist make adjustments to your treatment plan.
There are several tools and methods you can use to monitor your progress at home, including:
- Keeping a journal: Keeping a journal of your exercises, progress, and any changes in symptoms can help you track your progress over time.
- Taking measurements: Measuring your range of motion, strength, and flexibility regularly can help you see improvements and identify areas where you may need more work.
- Using apps: There are several apps available that can help you track your progress and provide feedback on your exercises.
- Working with a physiotherapist: Your physiotherapist can monitor your progress during each session and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
By monitoring your progress and staying committed to your home physiotherapy exercises, you can maximize your chances of a successful recovery and improve your overall physical function and mobility.
Potential Risks and Precautions
While home physiotherapy can be a safe and effective treatment option for many injuries, there are potential risks associated with performing exercises at home without professional supervision. Here are some potential risks associated with home physiotherapy:
- Reinjury: Without proper guidance, it is possible to perform exercises incorrectly or with too much intensity, which can lead to reinjury.
- Overuse injuries: Overusing the affected area during exercises can lead to pain, inflammation, and other overuse injuries.
- Safety hazards: Performing exercises in an unsafe environment or without proper equipment can lead to accidents or injuries.
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of home physiotherapy, here are some precautions to take:
- Work with a qualified physiotherapist: Working with a qualified and experienced physiotherapist can help to ensure that you are performing exercises correctly and safely.
- Start slowly: Start with low-intensity exercises and gradually increase the intensity and duration as your body becomes stronger and more flexible.
- Use proper equipment and techniques: Use proper equipment and techniques when performing exercises to reduce the risk of injury.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercises. If you experience pain or discomfort, stop the exercise and consult with your physiotherapist.
By taking these precautions and working closely with a physiotherapist, you can minimize the risks associated with home physiotherapy and maximize your chances of a successful recovery.
When to Seek Professional Help
While home physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option for many injuries, there may be cases where professional medical attention is necessary. Here are some signs that home physiotherapy may not be enough:
- Pain is getting worse: If your pain is getting worse or is not improving with home physiotherapy, it may be a sign that there is an underlying issue that requires medical attention.
- Loss of mobility: If you are experiencing a loss of mobility or range of motion, it may be a sign that there is an issue that requires medical attention.
- Signs of infection: If you experience signs of infection such as fever, chills, redness, swelling, or pus around the affected area, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
- Numbness or tingling: If you experience numbness or tingling in the affected area, it may be a sign of nerve damage and requires medical attention.
If you experience any of these signs, it is important to seek the help of a medical professional. A doctor or physiotherapist can assess your condition and determine if additional treatment is necessary. They may recommend additional testing, prescribe medication, or refer you to a specialist for further evaluation.
Remember, it is always better to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention if you have any concerns or questions about your condition.
Conclusion
Home physiotherapy can be a safe, effective, and convenient treatment option for a wide range of injuries. By performing exercises in the comfort of your own home, you can improve your physical function and mobility while avoiding the inconvenience and cost of in-clinic physiotherapy. Here are some of the key benefits of home physiotherapy:
- Comfort of familiar surroundings
- Flexibility of scheduling
- Cost-effectiveness compared to in-clinic physiotherapy
- Customized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs and goals
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of home physiotherapy, it is important to work closely with a qualified physiotherapist, follow proper techniques and precautions, and monitor your progress regularly. Remember, if you experience any signs of worsening pain or mobility, it is important to seek the help of a medical professional.
In conclusion, home physiotherapy can be a great option for those looking to recover from an injury in a comfortable, convenient, and cost-effective manner. By taking the necessary precautions and following your physiotherapist’s advice, you can speed up your recovery and improve your overall physical function and mobility.