
Ergonomic Training: How It Can Improve Your Health and Productivity
Ergonomic training is a critical component of workplace safety and overall health and wellness. It involves educating individuals on proper body mechanics, posture, and equipment use to reduce the risk of injury and improve productivity. The goal of ergonomic training is to optimize the interaction between workers and their environment, which can lead to numerous benefits for both the individual and the organization.
One of the primary benefits of ergonomic training is the prevention of workplace injuries. According to the National Safety Council, workplace injuries cost US businesses over $170 billion annually, and ergonomic-related injuries account for a significant portion of these costs. By educating workers on proper ergonomics, organizations can reduce the risk of injury and lower healthcare costs associated with workplace injuries.
Another benefit of ergonomic training is improved productivity. When individuals have the proper knowledge and tools to optimize their work environment, they can work more efficiently and with less fatigue. This leads to increased productivity, which can benefit both the individual and the organization.
In addition to the benefits within the workplace, ergonomic training can also improve overall health and wellness. By developing good habits and maintaining proper posture and body mechanics, individuals can reduce the risk of chronic pain and other musculoskeletal disorders. This can lead to improved quality of life and decreased healthcare costs associated with these conditions.
Overall, ergonomic training is a critical component of workplace safety and overall health and wellness. By optimizing the interaction between workers and their environment, organizations can reduce the risk of workplace injuries, increase productivity, and improve overall health and wellness.
The Importance of Ergonomics in the Workplace
The importance of ergonomics in the workplace cannot be overstated. Ergonomic training can significantly improve workplace safety and productivity, benefiting both the worker and the organization.

Workplace injuries are a major concern for organizations, and they can have significant financial and human costs. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, over 900,000 workplace injuries and illnesses resulted in time away from work in 2019 alone. These injuries can result in lost wages, medical expenses, and decreased productivity. In fact, a study by Liberty Mutual found that the most disabling workplace injuries cost US businesses $59 billion in 2019.
Ergonomic training can help prevent workplace injuries by teaching workers proper body mechanics, posture, and equipment use. By reducing the risk of injury, organizations can save money on workers’ compensation claims, medical expenses, and lost productivity.
In addition to improving workplace safety, ergonomic training can also increase productivity. When workers have the knowledge and tools to optimize their work environment, they can work more efficiently and with less fatigue. This can lead to increased productivity, improved quality of work, and increased job satisfaction.
Overall, the importance of ergonomic training in the workplace cannot be understated. By improving workplace safety and productivity, organizations can benefit both the worker and the organization. With the prevalence and cost of workplace injuries, ergonomic training is a critical investment for any organization that prioritizes the health and safety of their employees.
Common Workplace Hazards
There are several common workplace hazards that ergonomic training can help prevent. These hazards can lead to injuries and decreased productivity, making them a significant concern for organizations.
One of the most common workplace hazards is repetitive motion injuries. These injuries occur when workers perform the same motion repeatedly, leading to strain on the muscles, tendons, and nerves. Examples of repetitive motion injuries include carpal tunnel syndrome and tennis elbow. Ergonomic training can teach workers how to perform their tasks with less strain on their bodies, reducing the risk of repetitive motion injuries.
Another common workplace hazard is manual lifting and handling. Lifting heavy objects or performing repetitive lifting tasks can lead to strains and sprains. These injuries can be prevented by teaching workers proper lifting techniques and providing ergonomic lifting equipment, such as lift assists and adjustable height workstations.
Poor posture is another hazard that can lead to injuries and decreased productivity. When workers sit or stand in awkward positions for long periods, it can lead to pain and discomfort. Over time, poor posture can lead to chronic pain and musculoskeletal disorders. Ergonomic training can teach workers how to maintain proper posture and body mechanics, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall comfort.
Other common workplace hazards that ergonomic training can help prevent include slips, trips, and falls, exposure to vibration, and awkward or cramped workspaces. By educating workers on how to identify and prevent these hazards, organizations can improve workplace safety and productivity.
Overall, ergonomic training can help prevent several common workplace hazards that can lead to injuries and decreased productivity. By teaching workers how to perform their tasks with less strain on their bodies and how to maintain proper posture and body mechanics, organizations can create a safer and more comfortable work environment for their employees.
Proper Posture and Body Mechanics
Proper posture and body mechanics are critical components of ergonomic training. They can help prevent injuries and improve overall comfort and productivity in the workplace.
Maintaining proper posture is important because it helps distribute the weight of the body evenly and reduces the strain on muscles and joints. When workers sit or stand in awkward positions for long periods, it can lead to pain and discomfort. Over time, poor posture can lead to chronic pain and musculoskeletal disorders.
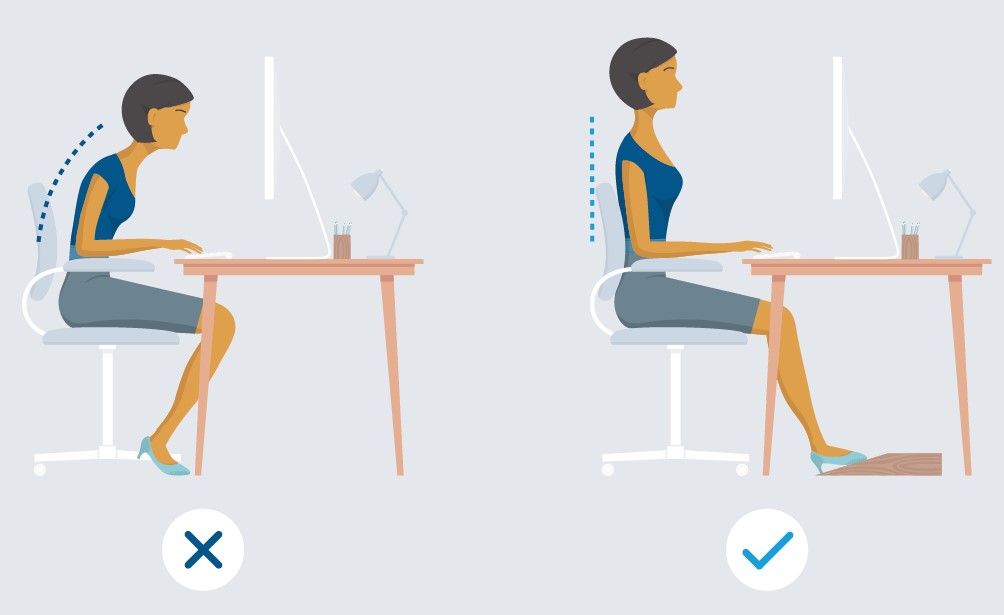
To maintain good posture, workers should keep their feet flat on the ground and their back straight. When sitting, they should use a chair with proper lumbar support and adjust the height so that their knees are level with their hips. Workers who stand for long periods should wear comfortable shoes with good arch support and shift their weight from one foot to the other regularly.
Body mechanics also play an important role in preventing injuries. Workers should use the largest muscles in their body to perform tasks, rather than relying on smaller muscles. For example, when lifting heavy objects, workers should use their legs to lift, rather than bending at the waist and using their back muscles.
To maintain good body mechanics, workers should keep their body aligned and avoid twisting or reaching when performing tasks. They should also avoid overreaching or bending their neck or back for extended periods. When working at a computer, workers should position the monitor so that the top of the screen is at or below eye level and the keyboard is at a comfortable distance from the body.
Overall, proper posture and body mechanics are essential for maintaining a healthy and comfortable work environment. By teaching workers how to maintain good posture and body mechanics, organizations can reduce the risk of injuries and improve overall productivity.
Equipment and Workstation Setup
Equipment and workstation setup are critical components of ergonomic training. The way equipment is arranged and used can significantly affect the ergonomics of a work environment.
Equipment that is poorly designed or adjusted can lead to awkward postures, excessive force, and repetitive motions. This can lead to pain and discomfort in the muscles and joints, as well as an increased risk of injury. On the other hand, equipment that is designed with ergonomics in mind can help prevent these problems and improve productivity.
When setting up a workstation, workers should make sure that the equipment is adjusted to fit their body size and shape. For example, the height of the chair, desk, and computer monitor should be adjustable to accommodate workers of different heights. The keyboard and mouse should be positioned so that the worker’s wrists are straight and their arms are relaxed.
Ergonomic equipment can also help improve posture and reduce the risk of injury. Examples of ergonomic equipment include ergonomic chairs, adjustable height workstations, and ergonomic keyboards and mice. When selecting ergonomic equipment, it is important to consider the individual needs of workers and choose equipment that fits their body size and shape.
Other tips for setting up a workstation and selecting ergonomic equipment include using document holders to reduce neck and eye strain, positioning the phone so that it is easy to reach, and using footrests to reduce pressure on the feet and legs. By paying attention to equipment and workstation setup, workers can improve their posture, reduce the risk of injury, and work more comfortably and productively.
Overall, equipment and workstation setup play a crucial role in ergonomics. By teaching workers how to set up their workstations and select ergonomic equipment, organizations can create a more comfortable and productive work environment.
Stretching and Exercise
Stretching and exercise are important components of ergonomic training. They can help improve flexibility, reduce the risk of injury, and increase overall comfort and productivity in the workplace.
Stretching can help prevent injuries by increasing flexibility and reducing muscle tension. When muscles are tight and inflexible, they are more susceptible to strain and injury. Stretching can help improve range of motion and reduce the risk of injury by loosening tight muscles and improving blood flow.
Examples of stretching exercises that can be incorporated into the workday include shoulder rolls, neck stretches, and wrist and finger stretches. These exercises can help reduce tension in the upper body and prevent repetitive motion injuries. They can also be done at a desk or workstation, making them easy to incorporate into the workday.
Exercise is also important for maintaining good health and preventing injuries. Regular exercise can help improve strength, flexibility, and endurance, which can all contribute to improved ergonomics and reduced risk of injury. Examples of exercises that can be incorporated into the workday include walking meetings, desk exercises, and standing desks.
Walking meetings involve taking a walk with colleagues rather than sitting in a conference room. Desk exercises, such as leg lifts or desk pushups, can be done during breaks or when transitioning between tasks. Standing desks allow workers to alternate between sitting and standing, which can help reduce the risk of injury from prolonged sitting.
Overall, stretching and exercise are essential components of ergonomic training. By incorporating stretching and exercise into the workday, workers can improve flexibility, reduce the risk of injury, and increase overall comfort and productivity.
Ergonomics Beyond the Workplace
Ergonomic habits can benefit overall health and wellness beyond the workplace. By incorporating ergonomic habits into daily life, individuals can reduce the risk of chronic pain and other musculoskeletal disorders, improve posture, and increase overall comfort and productivity.
One example of an ergonomic habit that can be incorporated into daily life is maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking. This can help reduce the risk of back pain, neck pain, and other musculoskeletal disorders. Additionally, regular exercise can help improve strength and flexibility, which can contribute to improved posture and reduced risk of injury.
Another example of an ergonomic habit is using proper lifting techniques when performing household tasks, such as lifting heavy objects or carrying groceries. Using the legs rather than the back to lift can help reduce the risk of injury and strain.
Other ergonomic habits to incorporate into daily life include taking frequent breaks when performing tasks that require prolonged sitting or standing, using a headset when talking on the phone to reduce neck and shoulder strain, and adjusting the height of computer monitors to reduce eye strain.
By incorporating ergonomic habits into daily life, individuals can improve overall health and wellness. These habits can help reduce the risk of chronic pain and musculoskeletal disorders, increase comfort and productivity, and improve overall quality of life.
Overall, ergonomics extends beyond the workplace and can benefit individuals in all areas of their lives. By incorporating ergonomic habits into daily life, individuals can improve their health and wellness and reduce the risk of injury and chronic pain.
Getting Started with Ergonomic Training
Getting started with ergonomic training can seem daunting, but it is an important investment in overall health and wellness. Here are some tips for getting started with ergonomic training and developing and maintaining ergonomic habits:
- Start with an ergonomic assessment: An ergonomic assessment can help identify areas of your workspace or daily routine that may be contributing to discomfort or injury. This can provide a starting point for making changes to improve ergonomics.
- Educate yourself: Learning about ergonomics and how to maintain proper posture and body mechanics is a critical first step in ergonomic training. There are many resources available, including online courses, books, and videos.
- Make changes gradually: It can be overwhelming to try to make all ergonomic changes at once. Start by making small changes, such as adjusting the height of your chair or taking more frequent breaks, and gradually build on these changes over time.
- Use ergonomic equipment: Ergonomic equipment, such as chairs, keyboards, and mice, can help reduce the risk of injury and improve comfort. Consider investing in ergonomic equipment that is appropriate for your needs.
- Incorporate stretching and exercise: Stretching and exercise can help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and prevent injuries. Incorporate stretching and exercise into your daily routine to improve ergonomics and overall health and wellness.
- Be mindful of your body: Pay attention to your body and how it feels throughout the day. Take breaks and make adjustments as needed to maintain good posture and prevent discomfort or injury.
Overall, developing and maintaining ergonomic habits takes time and effort, but it is an important investment in overall health and wellness. By starting with an ergonomic assessment, educating yourself, making changes gradually, using ergonomic equipment, incorporating stretching and exercise, and being mindful of your body, you can improve ergonomics and reduce the risk of injury and chronic pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ergonomic training is a critical investment in workplace safety and overall health and wellness. By teaching workers how to maintain proper posture and body mechanics, use ergonomic equipment, and incorporate stretching and exercise into their daily routines, organizations can reduce the risk of injury and improve productivity.
The benefits of ergonomic training extend beyond the workplace and can improve overall health and wellness. By incorporating ergonomic habits into daily life, individuals can reduce the risk of chronic pain and other musculoskeletal disorders, improve posture, and increase overall comfort and productivity.
It is important to start small and make changes gradually, as developing and maintaining ergonomic habits takes time and effort. By starting with an ergonomic assessment, educating yourself, using ergonomic equipment, and incorporating stretching and exercise into your daily routine, you can improve ergonomics and reduce the risk of injury and chronic pain.
In conclusion, ergonomic training is an investment in your health and well-being. By incorporating ergonomic habits into daily life, you can improve posture, reduce the risk of injury, and increase overall comfort and productivity. So start today and make small changes that will lead to significant improvements in your health and well-being.
